This article is more than one year old. Older articles may contain outdated content. Check that the information in the page has not become incorrect since its publication.
Manipulating Services Dynamically via QoS
Manipulating Services Dynamically via QoS
QoS (short form of Quality of Service), is a common terminology talking about network devices. For example, by adjusting and manipulating the weights of ports of a router dynamically via QoS, engineers could give priority to services running on these ports and make sure these services’ quality and reliability.
In Dubbo, QoS is used to query and manipulate services dynamically, like getting a list of active provider and consumer services, and launching or withdrawing services (i.e registering to or unregistering services from registration center).
Mechanism of QoS
From 2.5.8, QoS is introduced into Dubbo and is activated by default. All QoS’s features are abstracted to commands, which could be executed to get responses from QoS.
QoS is based on Netty4. In versions earlier than 2.6.x, Dubbo relies on Netty3, so you have to add Netty4 as a dependency explicitly to ensure that Netty4 works. If you generate a Dubbo application on http://start.dubbo.io, there’s no need to add configurations because Netty4 is listed as a dependency by default.
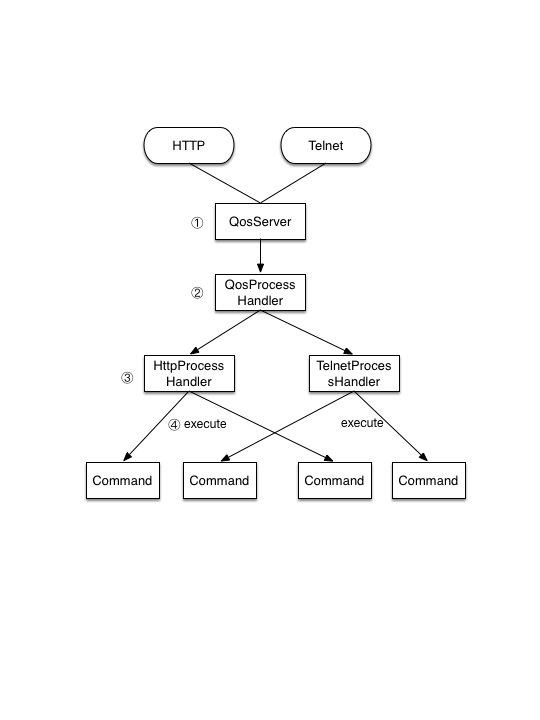
The picture above shows how QoS works:
- Start and listen to a port (22222 by default).
- Choose a corresponding request handler by detecting the protocol (telnet or http) a request comply with.
- Decode and parse the request to generate corresponding command according to the protocol.
- Execute commands and return with responses.
QoS Commands:
Commands that QoS supports at the current moment include:
help, list available commandsls: list all active provider services and consumer servicesonline: dynamically register a service or all services to registration centeroffline: dynamically remove (unregister) a services or all services from registration centerquit: quit the current telnet session
Now we are going to demonstrate how to manipulate services dynamically via QoS.
Access QoS via Telnet
Assuming that our Dubbo server has started, connect to it via telnet:
$ telnet localhost 22222
Trying 127.0.0.1...
Connected to localhost.
Escape character is '^]'.
????????? ??? ?? ??????????? ??????????? ????????
??? ???? ??? ??? ??? ??? ??? ??? ??? ???
??? ??? ??? ??? ??? ??? ??? ??? ??? ???
??? ??? ??? ??? ?????????? ?????????? ??? ???
??? ??? ??? ??? ??????????? ??????????? ??? ???
??? ??? ??? ??? ??? ??? ??? ??? ??? ???
??? ???? ??? ??? ??? ??? ??? ??? ??? ???
????????? ????????? ??????????? ??????????? ????????
dubbo>
A dubbo> prompt would show up once you connect to server. Now input help:
dubbo>help
+---------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| help | help command |
+---------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| ls | ls service |
+---------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| offline | offline dubbo |
+---------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| online | online dubbo |
+---------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| quit | quit telnet console |
+---------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
dubbo>
This command lists all available commands with explanations.
You can also use help to a specific command to read examples of that command.
dubbo>help online
+--------------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| COMMAND NAME | online |
+--------------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| EXAMPLE | online dubbo |
| | online xx.xx.xxx.service |
+--------------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
Use ls to check services’ status:
dubbo>ls
As Provider side:
+------------------------------------------+---+
| Provider Service Name |PUB|
+------------------------------------------+---+
|org.apache.dubbo.demo.provider.DemoService| Y |
+------------------------------------------+---+
As Consumer side:
+---------------------+---+
|Consumer Service Name|NUM|
+---------------------+---+
There is a service named org.apache.dubbo.demo.provider.DemoService in the provider side. PUB=Y in the second columns means that the service has been published to the registration center, waiting to be called by the consumer side.
Assuming that we need to withdraw a service dynamically, we can use offline command:
dubbo>offline org.apache.dubbo.demo.provider.DemoService
OK
You can see that the command responds with OK. Check the services’ status using ls:
dubbo>ls
As Provider side:
+------------------------------------------+---+
| Provider Service Name |PUB|
+------------------------------------------+---+
|org.apache.dubbo.demo.provider.DemoService| N |
+------------------------------------------+---+
As Consumer side:
+---------------------+---+
|Consumer Service Name|NUM|
+---------------------+---+
You can see that PUB of org.apache.dubbo.demo.provider.DemoService has been set to N.
Quit the current telnet session using quit:
dubbo>quit
BYE!
Connection closed by foreign host.
Access QoS via HTTP
In the example above we performed an offline action to org.apache.dubbo.demo.provider.DemoService. Now we are going to demonstrate how to register the service above via HTTP.
$ curl -i http://localhost:22222/online?service=org.apache.dubbo.demo.provider.DemoService
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: text/plain
Content-Length: 2
OK%
Beware of the parameters of online action. They need to be provided in the form of
key=value. However,keywould be ignored actually.
The action responds with OK. Now use ls to check providers’ status at the current moment.
$ curl -i http://localhost:22222/ls
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: text/plain
Content-Length: 365
As Provider side:
+------------------------------------------+---+
| Provider Service Name |PUB|
+------------------------------------------+---+
|org.apache.dubbo.demo.provider.DemoService| Y |
+------------------------------------------+---+
As Consumer side:
+---------------------+---+
|Consumer Service Name|NUM|
+---------------------+---+
You can see that the service’s PUB status has been changed to Y.
QoS’ Parameters
You can use parameters that QoS provides to config its startup. These parameters include:
| Parameter | Explanation | Default |
|---|---|---|
| qosEnable | Activate QoS or not | true |
| qosPort | The port QoS would bind to | 22222 |
| qosAcceptForeignIp | Enable remote access or not | false |
Attention. From 2.6.4/2.7.0,
qosAcceptForeignIpis set tofalseby default, because it’s risky if this property is set totrue. Think twice before you turn it on.
You can configure these parameters in the following ways:
- System property
dubbo.properties- XML
- Spring-boot auto configuration
They have priority in the following order: system property > dubbo.properties > XML > spring-boot.
System Property
-Ddubbo.application.qos.enable=true
-Ddubbo.application.qos.port=33333
-Ddubbo.application.qos.accept.foreign.ip=false
Dubbo.properties
Create a dubbo.properties file in this directory src/main/resources in your project, and copy the following codes into it:
dubbo.application.qos.enable=true
dubbo.application.qos.port=33333
dubbo.application.qos.accept.foreign.ip=false
XML
If you are going to config using XML, you can try this:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:dubbo="http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo/dubbo.xsd">
<dubbo:application name="demo-provider">
<dubbo:parameter key="qos.enable" value="true"/>
<dubbo:parameter key="qos.accept.foreign.ip" value="false"/>
<dubbo:parameter key="qos.port" value="33333"/>
</dubbo:application>
<dubbo:registry address="multicast://224.5.6.7:1234"/>
<dubbo:protocol name="dubbo" port="20880"/>
<dubbo:service interface="org.apache.dubbo.demo.provider.DemoService" ref="demoService"/>
<bean id="demoService" class="org.apache.dubbo.demo.provider.DemoServiceImpl"/>
</beans>
spring-boot auto configuration
If you are developing a spring-boot application, you can configure in application.properties or application.yml:
dubbo.application.qosEnable=true
dubbo.application.qosPort=33333
dubbo.application.qosAcceptForeignIp=false
